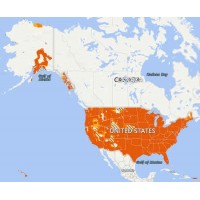
LTE Radios
LTE radios communicate through a proprietary cellular network (4G or LTE). These radios are NOT Push-to-Talk Cellular or PoC. Push-to-Talk Cellular uses the same cellular network that is used for cell phones. LTE uses a private cellular network. The advantage, or disadvantage, of LTE is your radios work anywhere cell phone coverage exists. This can even allow you to communicate across the country. Like regular two way radios, LTE radios offer one-on-many instant communication. However, in remote areas with no cell coverage these radios will not work. LTE radios require cellular service, which requires a monthly fee per radio. The monthly service contract is obtained through the radio dealer.
Perfect for those looking for the longest range possible and easy setup, such as companies operating vehicle fleets in large metropolitan areas.
Satellite Radios
Satellite radios connect through an array of satellites know as the Iridium satellite constellation. The Iridium satellite constellation is a system of 66 active satellites (and 9 spares in space) used for worldwide voice and data communication from hand-held satellite devices and other transceiver units. Satellite radios require a monthly service fee for the satellite usage. These devices can communicate globally and in back-country areas where most other forms of communication are not available.
Perfect for those needing global or back-country remote communications, such as gas and oil exploration, back-country search and rescue operations, or other other companies needing global communications in areas where infrastructure does not exist.
Network or WLan Radios
Network radios (also called Radio-Over-IP or RoIP) act like normal two way radios, but they communicate through the internet via a wireless internet connection on your computer network. We no longer carry these radios.
IP radios work well for businesses wanting to communicate within locations covered by their own computer network.





-200x200h.png)



